Quality Disclosure and Regulation: Scoring Design in Medicare Advantage
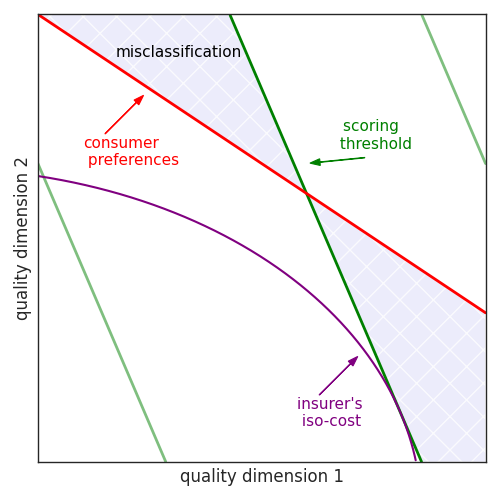
Policymakers and market intermediaries often use quality scores to alleviate asym- metric information about product quality. Scores affect the demand for quality and, in equilibrium, its supply. Equilibrium effects break the rule whereby more information is always better, and the optimal design of scores must account for them. In the context of Medicare Advantage, I find that consumers’ information is limited, and quality is inefficiently low. A simple design alleviates these issues and increases total welfare by 3.7 monthly premiums. More than half of the gains stem from scores’ effect on quality rather than information. Scores can outperform full-information outcomes by regulating inefficient oligopolistic quality provision, and a binary certification of quality attains 98% of this welfare. Scores are informative even when coarse; firms’ incentives are to produce quality at the scoring threshold, which consumers know. The primary design challenge of scores is to dictate thresholds and thus regulate quality.